A
Agile: Agile software development gathers several frameworks for software development under which requirements and solutions evolve through the collaborative effort of self-organizing and cross-functional teams and their customers. It is based on adaptive and iterative planning, evolutionary development, early delivery, and continual improvement. This enables rapid, flexible response to change and innovation. See my post
Agile Squad (same as Feature Team): an Agile Team dedicated to a long term mission that build features to the business. It works like a mini-startup. See my post.
Active Listening: listen to understand not just to answer with calm, kindness and genuine curiosity. See my post on the presentation of some coaching tools.
Artificial Intelligence (AI): sometimes called Machine Intelligence, is intelligence demonstrated by machines, in contrast to the natural intelligence displayed by humans and animals. It enables a machine to emulate cognitive processing and deliver tasks (nearly) like human being: perception, analysis, thinking, learning and adapting… A usual illustration is the understanding of the language and answering. See my post on Disruptive Technologies.
The Open API: is a public programming interface that allows you to share a resource (data, program, Web service…) to an authorized third party program. This enables interactions between different digital components and decouples services and data. See my post on Disruptive Technologies.
B
Big Data: Big Data refers to the use of advanced statistics and predictive analytics to correlate data, make sense of them and extract value from data now generated everywhere. The huge quantity of data is created internally to the company or externally. This new field requires new competences currently scarce (Data Scientists). See my post on Disruptive Technologies.
Blockchain: a technology for storing and transmitting information, taking form of a database that has the particularity of being distributed and shared simultaneously with all its users and which does not depend on any central body. It has the advantage of being fast, cheap, resilient, auditable and secure. Its scope is much broader than cryptocurrencies or cryptoassets: insurance, supply chain and logistic, energy, industry, health, etc… See my post on Disruptive Technologies.
Blue ocean strategy is the simultaneous pursuit of differentiation and low cost to open up a new market space and create new demand. It is about creating and capturing uncontested market space, thereby making the competition irrelevant. It is based on the view that market boundaries and industry structure are not a given and can be reconstructed by the actions and beliefs of industry players.
C
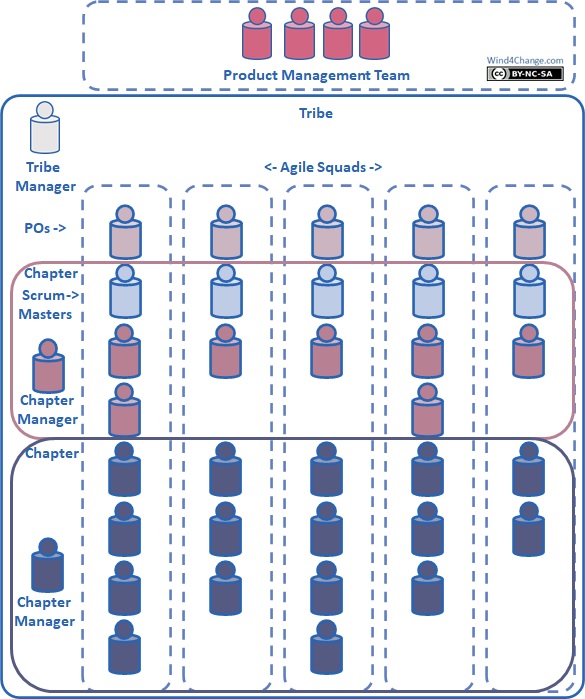
Chapter: a group of members of a Tribe having the same skills either functional of technical. The purpose of a Chapter is to develop skills of its members and to support sharing and consistency. Henrik Kniberg defines the Chapter as the glue between the Agile Squads. See my post.
Craftsmanship: is the state of art for software development. It is more than writing code meeting business and technical requirements (security, performance…). It is first a stance before being a set of technical skills. See my post. It involves the following practices: test
- Apply coding standards supporting sustainability of the code
- Embed early quality with early detection of bugs (functional and technical)
- Properly take into account production requirements since beginning
- Automate as far as possible
- Proceed by small steps to address complexity
John Kotter’s and Kurt Lewin‘s Changes Model: see my post.
Change Agent/Enabler: see my post.
Coaching: see my post.
The social and collaborative business: go to S section.
Cloud computing: is the on-demand computer system resources, especially data storage and computing power. It may even be billed based on use. See my post on Disruptive Technologies.
Customer experience (also known as CX): is defined by the interactions and experiences a customer has with a business throughout the entire customer journey, from first contact to becoming a long term satisfied customer. See my post.
Coopetition: with Digital, Partnership is not required any longer to reach the customers and your business partner may become your biggest competitor if that partner starts serving your customers directly. At the same time, you may need to cooperate with a direct rival due to interdependent business models or mutual challenges from outside your industry. A new word has been coined for that, coopetion that mixes cooperation and competition. See my post.
D
Design thinking: is an innovation process that covers from customer understanding to product development (see my post on innovation process).
DevOps: is more than just the automation of the software life-cycle from the creation to the deployment in production. It is first a close collaboration between developers and production operators to reach a seamless handover from development to production. See my post.
Disruption/disruptive technologies (term coined by Clayton Christensen): new technologies make it possible for new challengers and disrupters to enter the market. Business disruption happens when an existing industry faces a challenger that offers far greater value to the customer in a way that existing firms cannot compete with directly. See my post on Disruptive Technologies and Disruption and Value Volatility.
Data Revolution: Data are becoming the lifeblood of every departments and a strategic asset to be developed and deployed over time. Data are not any longer confined to the scope of specific business intelligence units. Smart connected objects are playing a role more and more important when talking about Data: they are data-driven and data-producing devices. Your organization must therefore be data-augmented in all its functions. See my post.
Dunbar’s numbers: refer to a cognitive limit to the number of people that one person can know and maintain social relationships with. Source Wikipedia.
For more on the Dunbar’s numbers, check my post about the Cognitive Load Theory.
E
The trust equation: the parameters to build a good relationship are Credibility, Reliability, Intimacy and No Personal Agenda. See my post on the presentation of some coaching tools.
F
Feature Team (same as Agile Squad): an Agile Team dedicated to a long term mission that build features to the business. It works like a mini-startup. See my post.
Fast IT gathers several concepts: Agile including early phases with Design Thinking approach, Craftsmanship, DevOps and relating tooling. It enables more value, speed and flexibility in building IT solutions by building quickly with a product delivered to the market, the MVP (Minimum Viable Product) and then by delivering continuously MMF (Minimum Marketable Features). See my post on Disruptive Technologies.
See other definitions and also my posts on Craftsmanship and DevOps.
Feedback: see my post on the presentation of some coaching tools.
G
Guild: A group of members across Tribes willing to share knowledge and good practices either functional or technical. It is a community of interest. It is complementary to Chapters to boost sharing. See my post.
The GROW Model: Goal, Reality, Options and Obstacles, Wrap Up/Way Forward/Will. See my post.
H
Horizontal Management: by the same convention in Agile at Scale, the chapters are displayed horizontally as they cross Agile Squads. When management is aligned with the Chapter it is then horizontal. See my post.
I
The influence model: see my post.
Internet of Things (IoT): stands for the extension of the Internet to things and places in the physical world. The object connected to the Internet is uniquely identified by the network like a computer connected to the Internet. It on-boards the intelligence required to generate data, captures them from its environment and automatically transfers them to the network. See my post on Disruptive Technologies.
Innovation Games: refer to a form of workshops developed by Luke Hohmann where customers play a set of directed games as a means of generating feedback about a product or service. Therefore, the data collected is gathered directly from customers or prospects and is intended to answer a specific question. The successful operation of an innovation game relies on collaborative play among the participants and a set of observers drawn from disparate functional groups within an organization. Source Wikipedia. To learn more check the book of Like Hohmann.
K
Kanban: see my post
L
Leagues: transversal consistency is enforced in the Tribe thanks to the chapters. Nevertheless, there are some transversal topics cross-Tribe requiring additional mechanisms. This is the case for Production and Architecture either functional or technical. This is the mission of the Leagues. See my post.
Lean Startup: similar to the principles of lean manufacturing and lean software development, the lean startup approach seeks to eliminate wasteful practices and increase value-producing ones during the earliest phases of a company. See my post on innovation process.
M
Minimum Marketable Feature (MMF): a small, self-contained feature that can be developed quickly and that delivers significant value to the user.
Minimum Viable Product (MVP): the minimum viable product is that version of a new product which allows a team to collect the maximum amount of validated learning about customers with the least effort.
O
Outcome-Driven Innovation (ODI): is a strategy and innovation process developed by Anthony W. Ulwick in 2005. It is built around the concept that people buy products and services to get jobs done. As people complete these jobs, they get measurable outcomes filling their needs. See my post on innovation process.
P
Product Owner (PO): the PO is the voice of the customers for the Agile Squad. He/she may rely on Subject Matter Experts to carry the VoC but he/she should know enough to prioritize the features and maximize value delivered by the Agile Squad. The PO validates the features potentially with the help of the SME. See my post on PO and PPO.
Proxy-Product Owner (PPO): « Proxy » stands for intermediary. The Proxy-PO act as an intermediary between the PO and the Agile Squad on some activities. See my post on PO and PPO.
PMT (Product Management Team): a PMT is the equivalent of the Product Owner but at the level of the Tribe. It is a group of senior business stakeholders plus the Tribe Manager. See my post.
3D printing: is much more than home 3D printers as it gathers all the concepts of materialization and simulation around the digital mock-up. It enables cheap and fast mock-ups but also the build of unit parts for a price that would be the price of building a series. Several materials are now available with different level of maturity: plastic, metal, concrete and even organic cells. See my post on Disruptive Technologies.
Platform Business Model: linear value chains are replaced by dynamic, networked ecosystems where data, information and value flow between all parties interacting. While a product is something you sell, a platform is the infrastructure empowered by new digital technologies that enables interactions between various actors. It creates a network effect where the value of the platform grows exponentially as the cooperation between other businesses or customers increases. See my post.
Project Management Paradigm changes with Agile at Scale: see my post.
Project Portfolio Management Paradigm changes with Agile at Scale: see my post.
Q
Powerful questions: see my post.
R
Roles reallocation with Agile at Scale: see my post.
S
Scrum: see my post
(Agile) Squad (same as Feature Team): an Agile Team dedicated to a long term mission that build features to the business. It works like a mini-startup. See my post.
Story Mapping: was invented by Jeff Patton. A story map is a simple but powerful way to arrange stories as a customer journey structured in business areas, features and at last user stories. See my post on innovation process.
Scale: Agile at Scale is aligning and cadencing a group of teams on the same business objective. It is different from just spreading agile foundations over a perimeter with frameworks like Scrum or Kanban. See my post on the introduction of Agile at Scale.
Scaled Agile Framework (SAFe), is a framework to guide enterprises in scaling lean and agile practices. It is one of the frameworks to do so like:
Spotify Model: is the Agile at Scale model coming from the company Spotify when scaling Agile. This model introduces IT delivery teams organized around features (Agile Squads or Feature Teams, displayed vertically) gathered in groups working for the same business (Tribes). This model has an horizontal dimension for all what is about knowledge building and sharing: the Chapters and the Guilds. Check in this glossary for the other definitions of the items coming from the Spotify Model: Agile Squads, Tribes, Chapters, Guilds…
Here is a collection of references about the Spotify Model:
- Henrik Kniberg’s original post on the Spotify return of experience.
- The direct link to Henrik Kniberg’s whitepaper on the Spotify return of experience.
- The link to the video Spotify engineering culture (part 1)
- The link to the video Spotify engineering culture (part 2)
Agile at Scale Synchronization Mechanisms: even if the Tribe and related Agile Squads have been designed to enforce autonomy and limit dependencies, there may be a need for synchronization mechanisms when several Agile Squads contribute to the same features or to features that are somehow connected. See my post.
The social and collaborative business: is the sharing or exchange of goods, services or knowledge between individuals through a digital platform. The transaction can be established with monetary exchange (collaborative business: sale, rental, service delivery) or without monetary exchange (social and solidarity business: donation, barter, mutual aid, volunteering). See my post on Disruptive Technologies.
T
T-Shape (skilling): like the shape of the T, the person has an expertise (the foot of the T) but in addition has basic knowledge in the other areas. See my post on Agile Squad.
Tribe: A Tribe is an incubator for mini-startups: a group of Agile Squads working on the same business area. The Tribe perimeter is defined to enforce autonomy and to limit dependencies with other Tribes. See my post.
The trust equation: the parameters to build a good relationship are Credibility, Reliability, Intimacy and No Personal Agenda. See my post on the presentation of some coaching tools.
V
A Value Chain is a set of activities that a firm operating in a specific industry performs in order to deliver a valuable product (i.e., good and/or service) for the market. The concept comes through business management and was first described by Michael Porter in his 1985 best-seller, Competitive Advantage: Creating and Sustaining Superior Performance.
Source Wikipedia.
VUCA stands for volatility, uncertainty, complexity and ambiguity. It was originally created in 1987, in the leadership domain by Warren Bennis and Burt Nanus. It was widespread by the US Army to describe the post cold war world. It is commonly used today especially in the Agile field.
- V – Volatility, changing quickly and often.
- U – Uncertainty, difficult to predict.
- C – Complexity, no cause-and-effect chain but multiple and interconnected factors.
- A – Ambiguity, unclear status, not black and white but shades of grey.
Source Wikipedia.
Aw, this was a very nice post. Taking a few minutes and actual effort to create a top notch
article… but what can I say… I hesitate a whole lot and never manage
to get anything done.