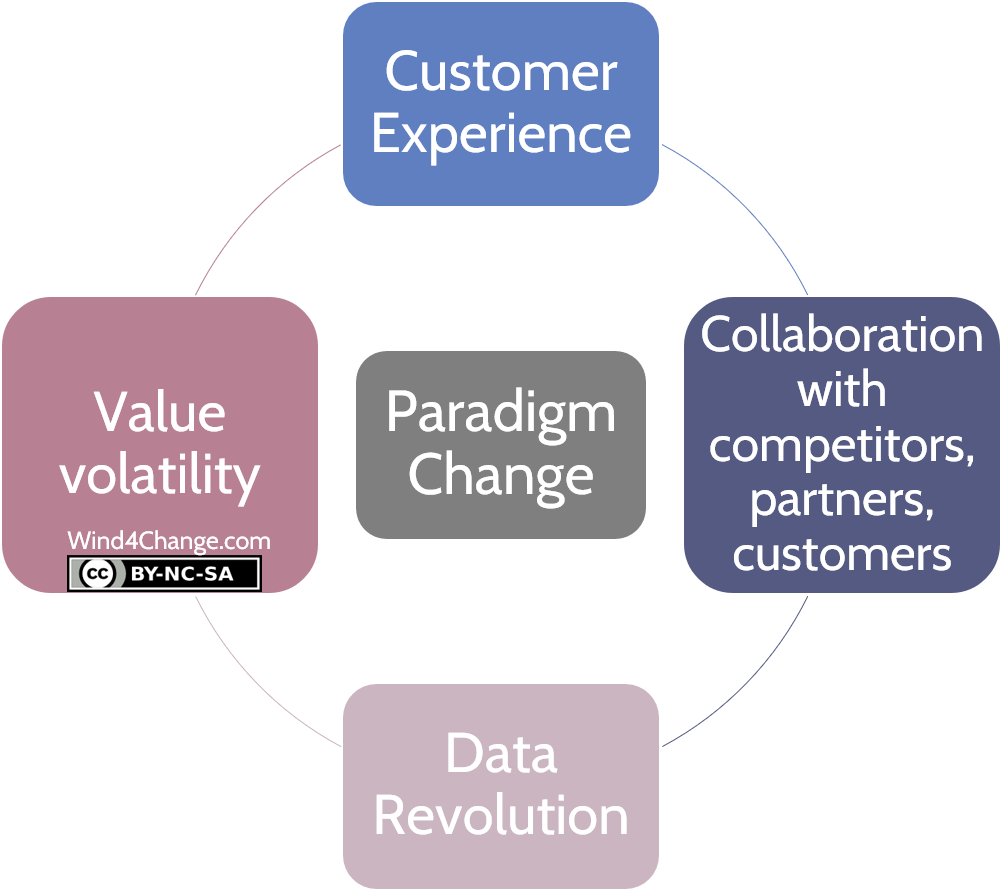
Coopetition and Digital Platform: Digital is more than the emergence of new disruptive technologies. It also involves a change of paradigm. The second one is the switch from binary relationships with other companies, either competition or collaboration, to coopetition. In addition, interactions with and between customers change to Network collaboration.
- Coopetion and Digital Platform
- Multiplayer integrated partnership empowered by BlockChain
- Customer Network
- What’s next? Learn more about Digital, the other new paradigms and the disruptive technologies
- Do you want to learn more about Coopetition this new form of collaboration and the Digital Platform Business Model? Here are some valuable references
Coopetion and Digital Platform
Coopetion

Traditionally, competition and cooperation are seen as opposites. To illustrate, businesses compete with rival businesses and they cooperate with supply chain partners who distribute their commodities or provide materials and parts for their production.
But with Digital, rules of the game change. Indeed, there is no need any more for Partnership to reach the customers. In addition, your business partner may become your biggest competitor if that partner starts serving your customers directly. At the same time, you may need to cooperate with a direct rival due to interdependent business models or mutual challenges from outside your industry.
In fact, a new word has been coined for that, coopetion that mixes cooperation and competition:
- Cooperate, to make your overall market grows in size and value
- Compete, to have the best share of this market
Digital Platform Business Model
Linear value chains are replaced by dynamic, networked ecosystems where data, information and value flow between all parties interacting.
While a product is something you sell, a platform is the infrastructure empowered by new digital technologies that enables interactions between various actors. Surely, it creates a network effect where the value of the platform grows exponentially as the cooperation between other businesses or customers increases.
A platform embodies coopetiton interactions for a given market.
Building a platform involves the following principles
- Become a trusted intermediary who brings together competing businesses and customers (e.g. Amazon Market place)
- Open up a proprietary product for other companies to build on (e.g. Android and Apple Application Stores)
- Build a new business whose value is created largely by its partners (e.g. Uber and Airbnb)
- Establish new partnerships or renegotiate existing ones to leverage platforms for distribution (e.g. The New York Times Company partnered with Facebook for distribution)
Multiplayer integrated partnership empowered by BlockChain
This one is not exactly a new Paradigm. But a significant improvement on the way cooperation happens over a value chain: faster, cheaper, more resilient, auditable and secured at the same time. And the Blockchain empowers this change.
We have introduce the blockchain with its characteristics in the first post of this series.
Let’s focus now on how Blockchain enhances cooperation on a value chain.
Multi-organization collaboration over the chain facilitated
Blockchain is designed to be distributed and synchronized across networks. So it makes it ideal for multi-organizational business networks such as supply chain or financial consortia. It also encourages organizations to come out from behind their firewalls and share data.
Common rules enforced for all the chain
You can’t just do whatever you want to the data. To illustrate, the types of transactions one can carry out are agreed between participants in advance and stored in the blockchain as “smart contracts”. As a result, this helps give confidence that everyone is playing by the rules.
Distributed trust enforced over the chain
Before one can execute a transaction, there must be agreement between all relevant parties that the transaction is valid. For example, if you’re registering the sale of a cow, that cow must belong to you or you won’t get agreement. This process is known as “consensus” and it helps keep inaccurate or potentially fraudulent transactions out of the blockchain.
Enhanced security of data over the chain even in comparison to traditional transactions with immutability of the data
Once you have agreed on a transaction and recorded it, it can never be changed. You can subsequently record another transaction about that asset to change its state. But you can never hide the original transaction. As a result, this gives the information about the provenance of products or assets. So, this means that for any, you can tell where it is, where it’s been and what has happened throughout its life.
Customer Network
Customers today are constantly connecting with and influencing each other and shaping business reputation and brands.
Really, Digital tools is changing how they discover, evaluate, buy, and use products. It is also impacting how they share, interact, and stay connected with brands.
The five new expectations coming with the Customer Networks
- Engage with digital content that is sensory, interactive, and relevant to their needs
- Customize their experiences by choosing and modifying a wide set of information, products, and services
- Connect with one another by sharing their experiences, ideas, and opinions through text, images, and social links
- Co-create on projects and goals through open plat
How to facilitate this paradigm change?
- Facilitate and leverage customer new expectations all over the customer journey.
- Go beyond driving potential customers to the stages of purchase (action) and repeat purchase (loyalty). To put it in other words: monitor and leverage the influence of satisfied customers for them to reach the stage of advocacy. Therefore, they will contribute to the growth of the business in the rest of its customer network.
What’s next? Learn more about Digital, the other new paradigms and the disruptive technologies
Check my other posts on Digital and the new paradigms:
- Customer Experience
- Coopetition and Digital Platform Business Model (this post)
- Data revolution
- Value volatility
And how Agile fits in the digital picture.
Check my post about the disruptive technologies this post refers to.
Learn about competition and strategy in digital platform context.
Do you want to learn more about Coopetition this new form of collaboration and the Digital Platform Business Model? Here are some valuable references
- A good post on the benefits of Blockchain
Excellent books about Digital
- Reinventing the Product
- The Digital Transformation Playbook
- The website of the author, David Rogers