Is Digital a bunch of new disruptive technologies? Or, is it a new way of doing business? Furthermore, how does agile fit in the picture?
In this first post of a serial of 6, we will review the disruptive technologies considered as part of the digital revolution. We will start with those that are Data Related: Big Data, Artificial Intelligence, Internet of Things and Cloud Computing. Then we will review Blockchain, Social & collaborative business and 3D. And at last, those directly connected to Continuous Delivery: Fast IT and Open API.
- Introducing the digital disruptive technologies
- Data related technologies
- Blockchain
- Social and collaborative business
- 3D
- Two technologies illustrating Continuous Delivery, Craftsmanship and DevOps
- What's next? Learn more about Digital and why there is more than just disruptive technologies
- Do you want to learn more about the disruptive technologies? Here are some valuable references
Introducing the digital disruptive technologies
For some people, digital is the emergence of new disruptive technologies.
What is a disruptive technology?
A disruptive innovation describes a process by which a product or service takes root initially in simple applications at the bottom of a market and then moves up market, eventually challenging established competitors.
So, what are those disruptive technologies? Let’s introduce those considered the most disruptive.
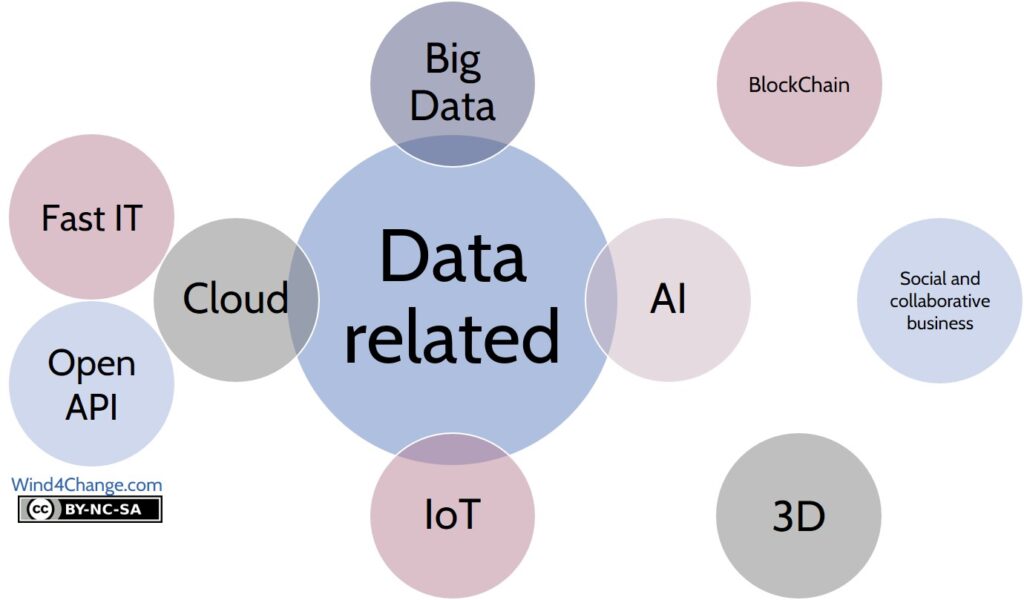
Data related technologies
Big Data
The term Big Data originally emerged as the field to manage data sets too large, too complex and changing too fast to be dealt with by traditional data-processing. Today, Big Data refers to the use of advanced statistics and predictive analytics to correlate data, make sense of them and extract value from data now generated everywhere. Surely, the huge quantity of data is created internally to the company or externally. As a result, this new field requires new competences currently scarce (Data Scientists).
Let’s use the DIKW model invented by Russell L. Ackoff to illustrate data life-cycle:
- Data: Raw Data have no meaning.
- Information: To evolve to information, Data should be processed to get a meaning and help answering the questions: Who, What, When and Where? Then, Data become useful for decisions and actions.
- Knowledge: To turn to knowledge, Data from multiple sources are combined over time. As a consequence, this enables answering the how question: how to use them? Knowledge is know-how: experience, expertise and skill.
- Wisdom: At last, Data switch in this model to Wisdom with more collecting and processing. This last step is a little bit more conceptual. As a result, Data make it possible to answer the why question: know the right things to do.
Artificial Intelligence – AI
Artificial Intelligence sometimes called Machine Intelligence, is intelligence demonstrated by machines, in contrast to the natural intelligence displayed by humans and animals.
It enables a machine to emulate cognitive processing and deliver tasks (nearly) like human being. These activities are perception, analysis, thinking, learning and adapting… To illustrate, an example is the understanding of the language and answering.
AI is accelerating today with the capacity to learn (machine learning) and the new architecture emulating neurons (deep learning). Surely, this new technology is quite useful to find patterns with data and give them sense and use. For instance, common implementations are chatbots enabling answering FAQ, autonomous cars, medical diagnosis…
Internet of Things – IoT
Considered the third evolution of the Internet, the Internet of Things (IoT) stands for the extension of the Internet to things and places in the physical world. The object connected to the Internet is uniquely identified by the network like a computer connected to the Internet. In addition, it on-boards the intelligence required to generate data (operating parameters, usage data, physical measurements, volume, etc.). Then it captures them from its environment and automatically transfers them to the network.
At the other end, there is a platform that centralizes and processes the data collected and manages the services created around them. Without a doubt, Big Data with support of AI are needed to manage this huge flow of data.
Connected objects empowers intelligent and autonomous devices such as the connected vehicle or smart home devices. They pave the way for new concepts such as the smart city, the factory of the future, connected health, etc.
They exponentially increase the volume of available and contextualized data. Truly, it is an opportunity for companies to transform their offer and related business model by integrating technology into their products.
IoT is a high-potential technology solution that faces two challenges:
- Threat of malicious behavior (hacking, remote takeover, etc.)
- Risk of breach of privacy
In addition, companies have still not identified the BtoB business case of this new technology.
Cloud computing
Cloud computing is the on-demand computer system resources, especially data storage and computing power. Moreover, it may even be billed based on use.
Cloud computing started 10 years ago and is now available in several forms: IaaS (infrastructure as a service), PaaS (platform), SaaS (software), and most recently CaaS (container) or FaaS (function)…
There is no longer a need to manage hardware that is handled as a virtual resource. In addition related software is delivered as a service. Surely, the term infrastructure as code illustrates this virtualization. In addition to reducing costs, this technology decreases complexity and increases flexibility.
Cloud computing is a game changer to manage the deluge of data describe above. Indeed, it provides big storage and computing capacity that can easily adapt to important variations over time. It supports other Digital Innovations but is critical to Big Data.
Blockchain

Blockchain is a technology for storing and transmitting information. It takes form of a database that has the particularity of being distributed and shared simultaneously with all its users and which does not depend on any central body. As a matter of fact, it has the advantage of being fast, cheap, resilient, auditable and secure. Its scope is much broader than cryptocurrencies or cryptoassets: insurance, supply chain and logistic, energy, industry, health, etc…
For instance, couple illustrations to make it more practical:
- Smart contracts, are like regular contracts except the rules of the contract are enforced in real-time on a blockchain. As a result, this eliminates middlemen and adds levels of accountability for all parties involved in a way impossible to traditional agreements.
- Supply chain and logistic,
- In manufacturing industry, allows transparency with a shared record of ownership and location of parts and products in real time.
- In food industry, enables transparency and efficiency of finding out what food might be contaminated and where throughout the supply chain.
- It enforces also provenance followup to ensure the sourcing of materials and production of products. So one can check that they adhere to the individual values of the members and also are not counterfeit.
- Insurance, supports law enforcement, insured and insurers to verify insurance coverage in real time and accelerate claims processing.
- Health, empowers the storage and utilization of electronic health records in order to deliver a complete tel-medicine experience. Surely, this enables to save time, money and duplication in procedures between a variety of facilities and providers.
Social and collaborative business

The social and collaborative business is the sharing or exchange of goods, services or knowledge between individuals through a digital platform. Furthermore, the transaction can be established with monetary exchange (collaborative business: sale, rental, service delivery) or without monetary exchange (social and solidarity business: donation, barter, mutual aid, volunteering).
Clearly, the success of this technology illustrates an evolution of consumption and behavior trends in our societies. Indeed, use and sharing tend to prevail over ownership. In addition, the use of an online community to solve a problem becomes commonplace (phenomenon of crowd-something).
3D
3D printing has become popular with home 3D printers. But 3D is much more than that as it gathers all the concepts of materialization and simulation around the digital mock-up.
It enables cheap and fast mock-ups but also the build of unit parts for a price that would be the price of building a series. In addition, several materials are now available with different level of maturity: plastic, metal, concrete and even organic cells. The size of the printers varies also a lot depending on the use!
3D can also be purely digital representation. For instance, 3D scanning of existing objects, holography and digital simulation removing the need of physical mock-ups for design. This also fastens innovation and decreases its cost.
Two technologies illustrating Continuous Delivery, Craftsmanship and DevOps
There is much more in Continuous Delivery than these 2 technologies but they illustrate the importance of this area.
Fast IT
Fast IT gathers several concepts: Agile including early phases with Design Thinking approach, Craftsmanship, DevOps and relating tooling. It enables more value, speed and flexibility in building IT solutions by building quickly with a product delivered to the market, the MVP (Minimum Viable Product) and then by delivering continuously MMF (Minimum Marketable Features). Teams are also aligned to the product to deliver. Certainly, this supports the objectives of value, speed and flexibility.
For more details on this area please, check may other posts on Agile, Craftsmanship and DevOps.
Open API
The Open API is a public programming interface that allows you to share a resource (data, program, Web service…) to an authorized third party program. As a consequence, this enables interactions between different digital components and decouples services and data.
It is an essential building block for digital services in the digital economy that is open, scalable with frequent changes and roll-outs. It is, at the same time, the current standard used within web services.
The web and technology giants (Google, IBM, Microsoft…) have grouped in an association, the Open API Initiative, to define a format and a standard open API description language. The term Open API also refers to this standard.
What’s next? Learn more about Digital and why there is more than just disruptive technologies
Check my other posts on Digital and the new paradigms:
And how Agile fits in the digital picture.
Do you want to learn more about the disruptive technologies? Here are some valuable references
Disruptive innovations
- Key concepts on disruptive innovations by the creator of the term, Clayton Christensen
Disruptive technologies
- SYNTEC whitebook in french: Révolution digitale
I leave a comment whenever I especially enjoy a article
on a website or if I have something to contribute to the conversation. It’s caused by the passion communicated in the post I browsed.
And on this post What is digital? What are the new disruptive technologies?
– Wind4Change. I was excited enough to drop a thought
😉 I do have a couple of questions for you if it’s allright.
Is it just me or does it look like a few of the remarks
come across like they are coming from brain dead visitors?
😛 And, if you are posting on additional places, I’d like to follow anything new you have to post.
Would you make a list all of your community pages like your
twitter feed, Facebook page or linkedin profile?
Hello, I am happy to read that you have appreciated this post around digital and the disruptive technologies.